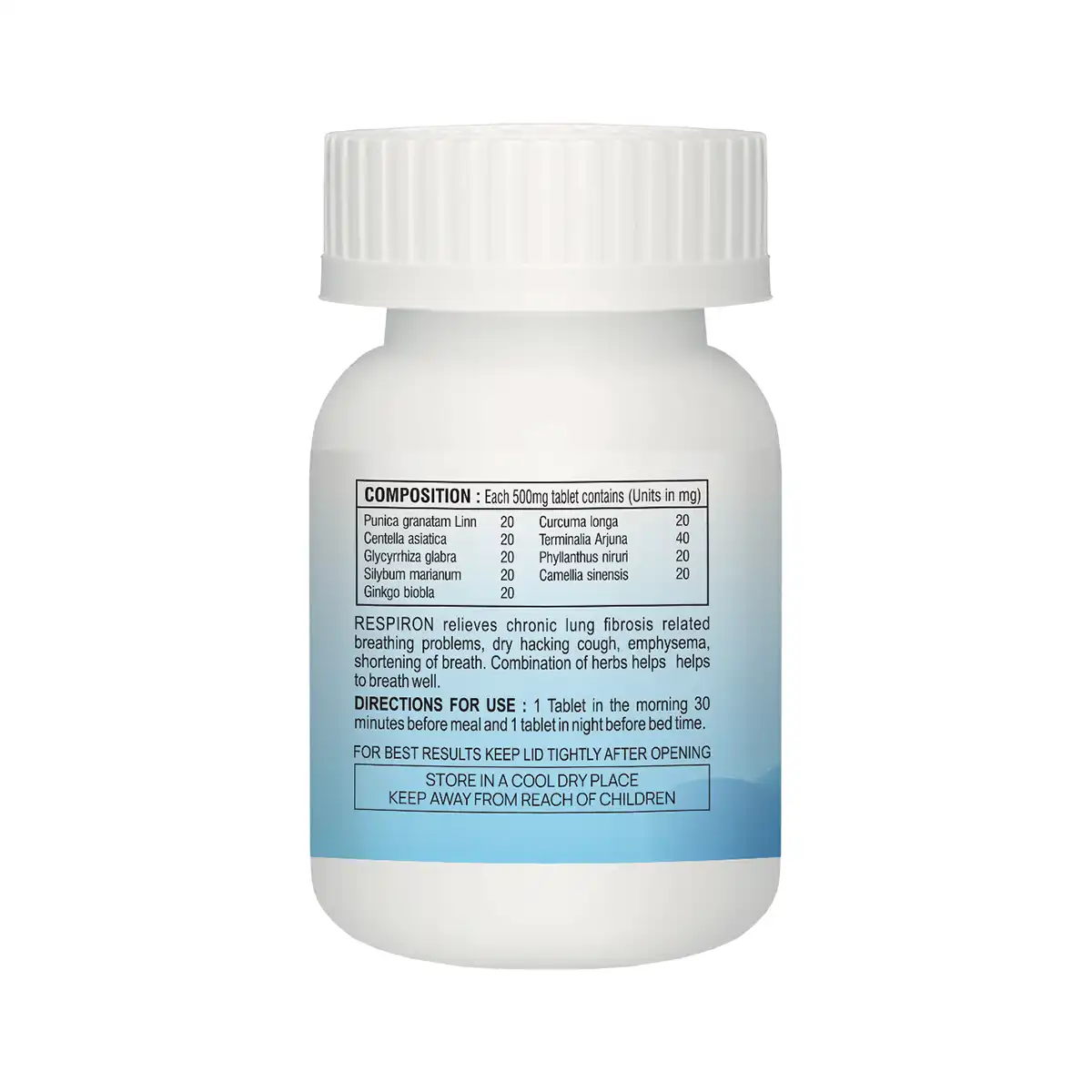
RESPIRON is an herbal formulation for lung fibrosis, breathing problems due to COPD, emphysema and chronic coughing, chronic coughing, poor breathing, dry hacking cough. Unique combination of herbs helps in improving poor breathing, chronic coughing, respiratory problems due to fibrosis, emphysema and provides easy breathing.
Indications (Benefits): Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Emphysema, Poor breathing, Hacking cough
Dosage: One tablet, twice daily, morning and evening 30 min. before meal
Product Attributes: 500mg, Tablet
Pack size: 30 tablets/bottle
Ingredients: Punica granatam Linn, Centella asiatica ,Glycyrrhiza glabra ,Silybum marianum ,Ginkgo biobla,Curcuma longa ,Terminalia Arjuna
Safety: Safe to use for children and adults. No side effects and allergies.
Chronic lung diseases are known to dramatically change the quality of one’s life, impact their energy levels, and sometimes, even impact their appearance. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) are known to cause shortness of breath due to obstructed airflow from the lungs.
Implications of chronic and/or repetitive microinjuries of epithelial cells are due to environmental pollutants such as cigarette smoke and viral infections of the alveolar epithelium. Microinjuries lead to chronic bronchitis which causes inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes, that carry air to and from the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs. It is characterized by daily cough and mucus (sputum) production.
In the later stage of the disease, epithelial damage is followed by injury and/or activation of cells lining the vascular (capillary endothelial cells, pericytes) and interstitial (resident mesenchymal cells including alveolar fibroblasts) compartments of the lung, as well as the epithelium of distal airways and resident macrophages. Eventually, lung mesenchymal cells accumulate, undergo and differentiate to myofibroblasts, which are considered the effector cells of fibrogenesis.
Clinical symptoms are shortness of breath, especially during physical activities, wheezing, chest tightness, chronic cough that may produce mucus (sputum) that may be clear, white, yellow or greenish, frequent respiratory infections and lack of energy. The clinical expression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is directly related to multiple alterations in lung function by excessive accumulation of inflammatory cell infiltration, edema, congestion and injury of alveolar epithelial cells, abnormal proliferation of ECM-producing cells (mesenchymal cells including fibroblasts and myofibroblasts, the overproduction of ECM (collagens, laminin, tenascin-C, etc.), resulting in progressive scarring and loss of lung function. These alterations derive from a complex disease process affecting all compartments of the lower respiratory system, from the conducting airways to the lung vasculature.
Chronic inflammation due to pollution induced micro-injuries is a pivotal etiology for COPD. Unique phytochemicals help in reducing inflammation, reducing fibrosis and slowing down EMT transition of the lung tissue. Shikonin found in alkanet root attenuates smoke-induced lung pathological changes, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) productions, and tissue damages caused by oxidative stress. Baicalin and baicalein found in Scutellaria baicalensis blocks TNF-α and IL-1, reduce TGF-β1, TNF-α, IL-6 and increases IL-10 (anti-inflammatory cytokine). Sulforaphane, luteolin, celastrol, curcumin, arctigenin inhibit β-catenin signaling pathways.
Transforming growth factor (TGF) ‑β1, a key profibrotic mediator, serves a critical role in inflammatory injury and repair, contributing to the development of airway remodeling in COPD. Inhibiting the TGF‑β1/Smad signaling pathway may lead to novel therapeutic strategies. Cordycepin found in Cordyceps militaris significantly inhibits transforming growth factor- (TGF-) and bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP-4) and regulates Smad signaling.
Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) is an active process in both small and large airways of patients with COPD and was related to the reduction of lung function in COPD. Several actives, like Salvianolic acid-A and plumbagin, block oxidative stress, while honokiol, gallic acid, piperlongumine, brusatol and paeoniflorin inhibit EMT transcription factors such as SNAIL, TWIST and ZEB. Resveratrol, genistein, baicalin, polyphyllin I, cairicoside E, luteolin, berberine, nimbolide, curcumin, withaferin-A, jatrophone, ginsenoside-Rb1, parthenolide, phoyunnanin-E, epicatechin-3-gallate, gigantol, eupatolide, baicalin and baicalein inhibit EMT acting on other signaling pathways (SIRT1, p38 MAPK, NFAT1, SMAD, IL-6, STAT3, AQP5, notch 1, PI3K/Akt, Wnt/β-catenin, NF-κB, FAK/AKT, Hh).
Applied For
Lung fibrosis, Emphysema, poor breathing, chronic coughing, shortening and breathing problems, chronic and dry hacking cough, respiratory problems due to fibrosis, COPD







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.