ERYTHEM is a formulary blend of nutraceuticals and herbs designed for immunomodulation and controlling inflammation by inhibiting excessive immune cell infiltration and related secondary pathology. ERYTHEM improves from excessive skin cell proliferation, skin inflammation and itching due to allergic responses. ERYTHEM manages skin ailments by correcting immunity and controlling inflammation, excessive immune cells infiltrations and hyper proliferation of skin cells with cytokine modulation and T cell population. The formulation slows down abnormal growth of cells as well as reduce over excessive cell infiltrations by correcting the modulating microenvironment of the skin.
Indications (Benefits): Itchy skin, Scaling, Redness, Pruritis, Eczema
Dosage: One capsule twice daily, morning and evening 30 min. before meal
Product Attributes: 500mg, Capsule
Pack size: 60 Capsules/Bottle
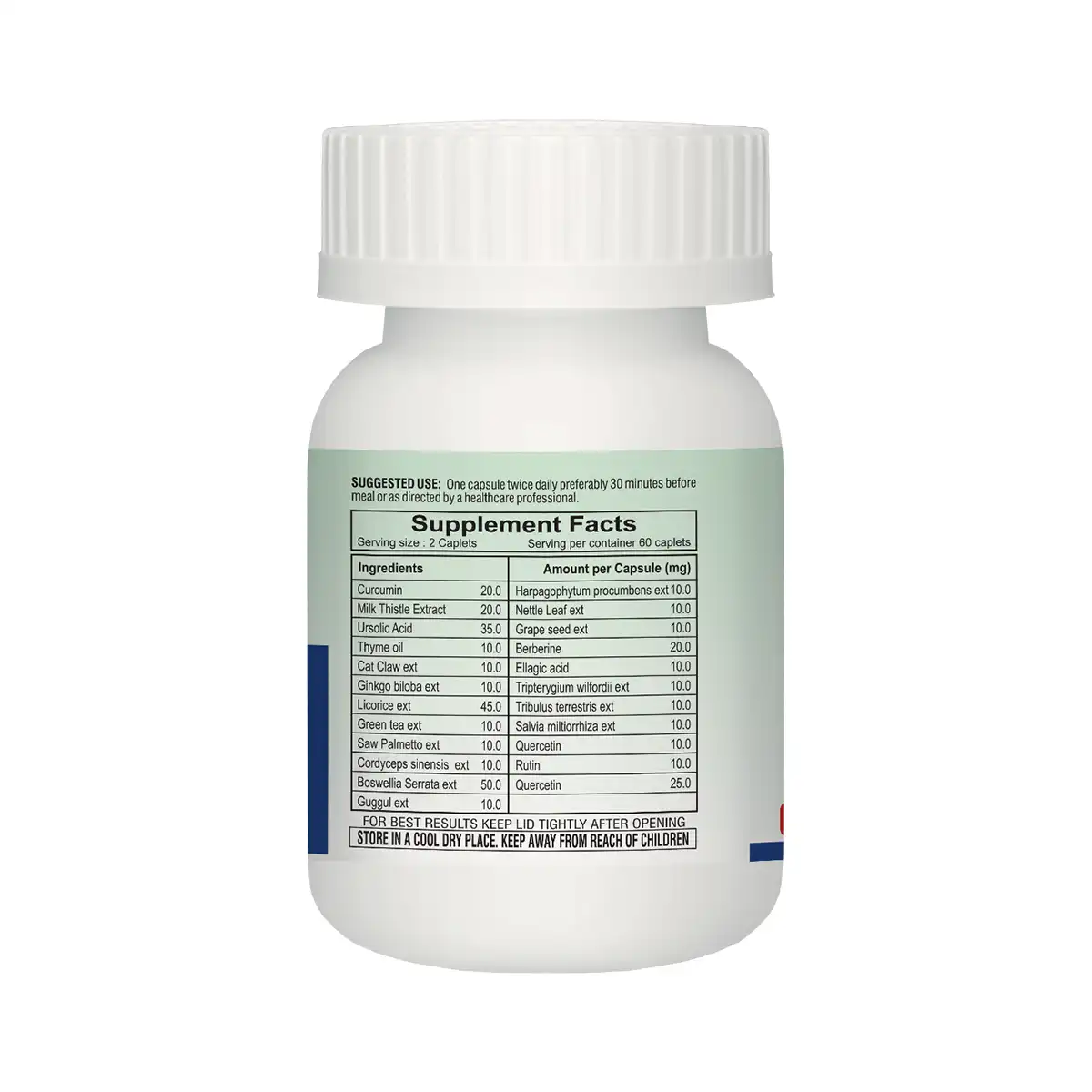
Ingredients: Milk Thistle Extract,Ursolic Acid,Curcumin,Cat Claw ext,Ginkgo biloba ext, Licorice ext, Saw Palmetto ext,Boswellia serrata ext, Harpagophytum procumbens ext, Nettle Leaf ext, Berberine, Tripterygium wilfordii ext, Quercetin, Rutin
Safety: Safe to use for adults. No side effects and allergies
There are many different types of skin-related autoimmune disorders, including scleroderma, psoriasis, SLE, dermatomyositis, allergic dermatitis, epidermolysis bullosa, and bullous pemphigoid. Autoimmune skin diseases occur because the body’s immune system attacks its own healthy tissues. There are abnormal infiltration of immune cells and cause different pathologies as per autoantigens are involved. There will be excessive immune cells as eosinophils where there are allergic responses. Another autoimmune T cells infiltration to cellular proteins and cell cementing substances cause different pathologies as keratinocytes proliferation in psoriasis, the immune system attacking the connective tissue under the skin and around internal organs and blood vessels. This causes scarring and thickening of the tissue in these areas and named as scleroderma. Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) where the immune system attacks its own tissues, causing widespread skin inflammation and tissue damage in the affected organs. Dermatomyositis, where immune system goes after the blood vessels inside your muscles and the connective tissues in skin. Epidermolysis Bullosa where cells infiltrate can be found around vessels, around follicles and in the interstitium. Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a blistering skin disease characterized by an autoimmune response to hemi-desmosomal proteins within the dermal-epidermal junction.
These skin conditions are pivotal to immune cell infiltrations and related secondary pathologies. These autoimmune and allergic conditions can be improved by inhibiting excessive immune cell infiltrations. This cellular infiltration can be inhibited with cytokine modulation, chemokine (the molecule which cause attraction of immune cells to pathological site) inhibition and modulate immune reactivity with promoting Treg cells. FOXP3+ Treg cells are found to modulate not only overactive TH17 cells but also slow down allergic eosinophils. The contribution of distorted immune activation has been proved to target some key immune components, namely IL-23, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and the Th17/IL-23 axis. The infiltrated psoriatic lesions have significantly increased levels of the CD4 T-cell subsets T helper (Th)1 and Th17. The immune genes are responsible for several functions that involve innate immunity, antigen presentation, the interleukin (IL)-23 axis, and T-cell development and polarization. TNF-α is a pro-inflammatory cytokine, produced by different cell types including lymphocytes, keratinocytes, endothelial cells, and macrophages, which amplifies inflammation response through several pathways.
Patients with overactive skin ailments are identified IL-17 as a key pathway that can be modulated by treatment with Indigo naturalis. Clinical studies have demonstrated that Indigo naturalis used as topical monotherapy is efficacious in treating patients with mild-to-moderate psoriasis, although the validity of these studies is challenged by intra-patient treatment comparison designs. One component of Indigo naturalis, indirubin, was reported to inhibit cyclin-dependent kinase and signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) activities, and keratinocyte proliferation. Moreover, Indigo naturalis extract has been shown to inhibit oxygen generation and elastase release in formyl-methionyl-leucylphenylalanine- induced human neutrophils in vitro. Indigo naturalis significantly down-regulated the IL-17 pathway in affected skin, similar to other therapies that successfully target this pathway. Moreover, we showed that one of the chemical components in Indigo naturalis, tryptanthrin, possesses moderate anti-IL-17 activity.
Curcumin is a polyphenol derived from the golden spice turmeric (“Curcuma longa”). Because of its numerous properties (e.g. anti – oxidant, anti -proliferative, anti-inflammatory), curcumin has been used for the treatment of psoriasis. The anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin have been showed in the serum as a decrease of more than 50% in the level of inflammatory factors, including TNF – α, IFN – γ, IL – 2, IL – 12, IL – 22 and IL – 23.
Argemone mexicana plant, and the fractions obtained from leaves and stem of Argemone mexicana plant, exhibit immunomodulation, lymphoproliferation inhibition, cytokine modulation such as IL-2 inhibition, IFN- inhibition, IL-10 induction, keratinocyte proliferation inhibition, keratolytic activity, endothelial cell proliferation inhibition, inhibition of cell adhesion molecule expression such as ICAM-1, MEST inhibition, and enzymes inhibition such as p60src Tyrosine kinase, which are known to be involved in anti-psoriatic activity and the usefulness of the extracts and fractions for the treatment and prevention of skin ailments.
Thymol and carvacrol suppress an antigen-specific immune response in vivo, in part, by inducing reductions in TH1, TH2 and TH17 cell-related cytokines and key transcription factors involved in their differentiation. Salvianolic acid A suppressed skin hypertrophy and decreased mast cell infiltration into skin lesions via chemokine inhibition. Triptolide and tripterine from Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides are known for suppressed expression of IFN-γ receptor α and blocked IFN‐γ signal transduction in keratinocytes via JAK2/STAT1 Pathway. Berberine is known for inhibition of infiltration of eosinophils into the dermis.
Applied For
• A new immuno-editing formulation for management of skin lesions
• Normalize skin microenvironment at the cellular level
• Support healthy immune cells to control excessive skin cells proliferation
• Balance TH17/IL-23 axis to subside excessive inflammatory cytokine production
• Enhance Treg cells to control immune over activation and abnormal cellular infiltration at the lesion site








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.